Overcoming ncAA Production Bottlenecks: High-Titer Antibody Expression With 100% pAzF Incorporation At Scale And Minimal Host Toxicity
Expanding the genetic code of therapeutic proteins with non-canonical amino acids (ncAAs) offers a precise way to build complex bioconjugates and site-specific antibody-drug conjugates. While host toxicity and low yields traditionally hinder large-scale production, a platform-based approach using Pseudomonas fluorescens demonstrates that high-titer expression is achievable.
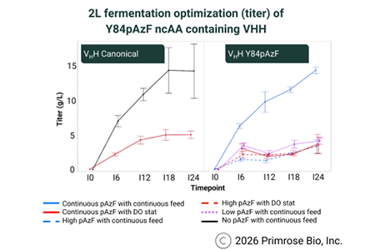
By leveraging hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS), researchers can pinpoint solvent-accessible regions for ncAA incorporation, ensuring protein functionality and binding affinity remain intact. Optimized continuous feeding strategies now allow for 15 g/L titers and 100% ncAA incorporation, successfully bridging the gap between lab-scale discovery and commercial-scale manufacturing.
Review this scientific poster to see how these advancements maintain production economics while expanding therapeutic potential.
Get unlimited access to:
Enter your credentials below to log in. Not yet a member of Bioprocess Online? Subscribe today.
