Optimal Microbial Sampling Criteria
By Giulia Artalli and Mark Hallworth
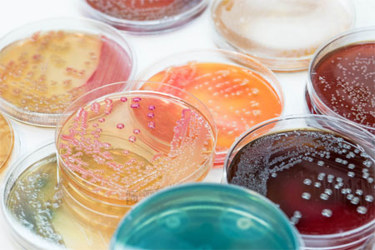
Microbiological sampling in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities is a critical component of environmental monitoring and is conducted using several distinct methods. These include surface sampling, passive aerosol (air) environmental sampling, and active aerosol (air) environmental sampling. Each of these techniques involves the collection of microorganisms on a growth medium, typically agar, where microbial colonies can develop and be quantified. While the underlying principle—cultivating microbes on a nutrient-rich surface—is consistent across methods, the instruments and procedures used vary significantly depending on the sampling approach.
It is important to understand that no single sampling method can independently confirm asepsis. Instead, a comprehensive sterility assurance strategy requires the integration of data from all sampling methods. This holistic approach is emphasized in the current version of the EU GMP Annex 1: 2022, which outlines regulatory expectations for maintaining sterile conditions in pharmaceutical environments. The regulation also provides more detailed guidance on specific aspects of environmental monitoring, including surface sampling and passive monitoring using settle plates.
Get unlimited access to:
Enter your credentials below to log in. Not yet a member of Bioprocess Online? Subscribe today.
