Modular And Single-use Tech Driving The Future Of Biomanufacturing
By Erica Friedman, senior research analyst, BioPlan Associates

Over the past 20 years that our Annual Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Report1 has measured adoption of single-use systems (SUS) and modular technologies in bioprocessing, they have clearly become critical to bioprocessing. The trend continues to be driven by demand for efficiency and flexibility and the need for more innovative manufacturing. Although starting with mainstream mAb production, these technologies are even more critical for cell and gene therapies, where small-scale SUS applications may be the only option.
As with single-use technologies, modular systems offer greater flexibility and can reduce capital costs, while more quickly increasing productivity and capacity. They can also reduce risks and improve product quality.
Our findings show that close to two-thirds of our annual report interviewees, including cell and gene developers and mAb developers, agree that cell and gene therapy is the sector most open to modular production. The remaining one-third either think therapeutic modalities do not matter or mAb and vaccine makers will like modular production more as their processes become more standard.
Disposable or single-use equipment is currently being used for almost every bioprocessing application and in every phase of manufacturing. While COVID-19 accelerated this trend, it has been steadily climbing since 2003, when BioPlan began surveying manufacturers and contract manufacturing organizations to evaluate trends in adoption and use of disposable/single-use systems in their biopharmaceutical manufacturing.
According to the annual study, in 2023 29.1% of biotherapeutic innovators indicated, “develop more modularized” production systems as a key area to avoid capacity constraints (See Fig 1). This percentage has been relatively consistent since 2007 when we first measured this factor. Interest in modular bioproduction has remained a consistent factor. Our study also indicated that Western European facilities in particular were significantly more interested in modular technologies than U.S. respondents, with 48.3% indicating interest in easing capacity problems.
Cost-effectiveness of SUS devices was the No. 1 factor for both biomanufacturers and CDMOs, with around 40% of respondents from each group expecting less expensive SUS technologies to reduce capacity problems. This interest in more cost-effective SUS suggests that if the technology were cheaper, greater utilization could be expected.
Fig 1: Single-use and Modular Facilities’ Role in Avoiding Capacity Constraints; Biomanufacturers vs. CDMOs (Selected Factors)
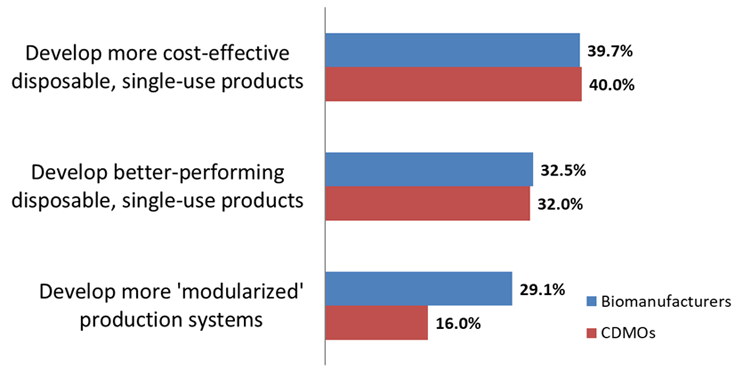
Source: 20th Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Capacity, BioPlan Associates Inc. April 2023
Adoption of single-use and modular bioprocessing systems for commercial manufacturing will accelerate the trend of building regional manufacturing facilities. Industry players may decide post-COVID-19 that more regional manufacturing facilities could reduce supply chain risks by avoiding shutdowns due to pandemics or other economic and political instability. Biomanufacturing facilities are being built as backups, particularly with larger companies. As biomanufacturing is performed at multiple facilities, companies are working to standardize their manufacturing platforms. Having second-source facilities actively manufacturing or serving as backups increases interest in single-use and modular bioprocessing platforms for commercial-scale production.
Multiple bioprocessing equipment developers and vendors are developing and marketing modular approaches to bioprocessing. Construction of new bioprocessing facilities, even for commercial manufacturing, can be completed in months compared to years. Companies are trying to develop bioprocessing systems using customizable modules ready for plug-and-play applications. In fact, nearly 14% of the industry is planning to evaluate upstream modular bioprocessing units within the next 12 months.
Modular: The Next Trend After Single-Use
The next step in the bioprocess industry’s evolution after single-use systems is likely to include modular bioprocessing units that compartmentalize unit process equipment, such as increased use of isolators and restricted access barrier systems. Major biopharmaceutical manufacturers are starting to adopt modular facilities. Enclosing bioprocessing equipment within their own isolator cabinets or enclosures or even free-standing modular buildings can significantly reduce risks of contamination and costs, including allowing use of cheaper, lower-grade cleanrooms housing this equipment. Companies including Cytiva, G-Con, and Pharmadule are marketing modular bioprocessing units. These essentially are single-use systems installed within a portable self-enclosed trailer or other deliverable room-sized cleanroom. Here, not just the equipment, but the cleanroom or unit that houses it are potentially single campaign or product-use and potentially disposable.
But in general, the core structure remains permanent while the equipment housed in modular units will be single-use and repeatedly replaced. True single use of modular bioprocessing units is likely more relevant to applications such as biodefense and epidemic vaccine manufacturing and under the following conditions:
- Needs are dire and demand a rapid response.
- Needs may be transitory, such as until an epidemic is under control.
- Safety hazards are involved.
- Facilities need to be rapidly set up on-site or near areas experiencing outbreaks.
Bioprocessing has also become much more portable, and facilities more cloneable, through modular bioprocessing systems. As smaller continuous bioprocess lines are introduced using smaller facilities, we expect this will increasingly create niches for SUS and modular platforms for commercial manufacturing.
Fig 2: Most needed cell therapy manufacturing improvements, systems, platforms, and infrastructure (2019-23, selected factors)
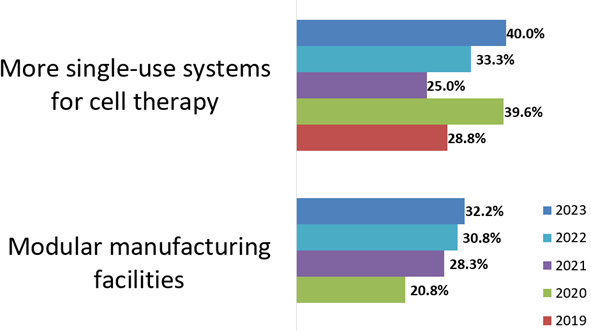
Source: 20th Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Capacity, BioPlan Associates, Inc. April 2023
For 2023, we see moderate point increases in multiple areas regarding improvements in cell therapy manufacturing. These include more single-use systems for cell therapy, better allogeneic bioprocessing technologies, and modular manufacturing facilities. Considering the relative novelty of innovative cell therapy bioprocessing, these factors involving single-use and modular bioprocessing likely map out the future platform technologies to be expected.
SUS Growth Trends In Biomanufacturing
Many of the single-use-related trends we found in this year’s annual report point to higher growth rates. For example, in continuous bioprocessing, 79.0% of respondents said that the industry will see fully-continuous, commercial-scale manufacturing facilities within five years. Additionally, 71.7% of respondents noted that continuous downstream processing systems should be single-use, up from 67% in 2022.
These trends support the relatively strong average annual growth rate in application first usage within facilities for disposables. In 2023, single-use device classes surveyed continue to have a positive growth rate for use within respondents’ facilities in four key categories where we saw virtually no change or very slight declines in growth this year:
Fig 3: Compound annual growth rate of adoption and first usage, (2006-23, selected disposables)
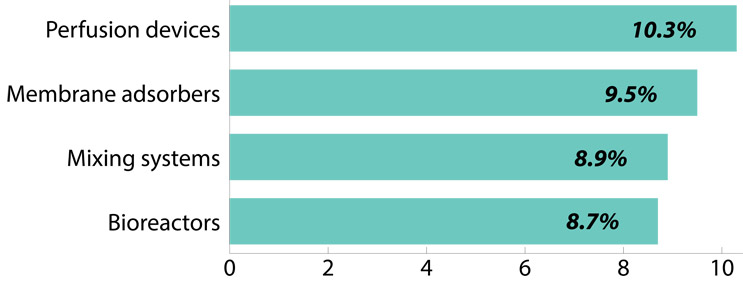
Source: 20th Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Capacity, BioPlan Associates, Inc. April 2023
- Perfusion devices continue to see an uptick in the average growth of the adoption and first usage of these devices over the past 17 years, since 2006, with a CAGR of 10.3%.
- Membrane adsorbers also see positive growth this year, with a 17-year CAGR of 9.5%.
- Mixing systems continued to grow, showing at 8.9% CAGR.
- SUS bioreactors are steadily growing at 8.7% CAGR since 2006.
SUS equipment, with the greatest growth rate over time, tends to include complex devices, and their usage growth over this period shows consistency, especially since they were relatively new technologies in the early 2000s. In contrast, disposable filter cartridges saw the lowest growth with 0.8% over the past 17 years. This is because filters were common SUS devices, even back in 2006, so they reached a saturation point relatively early on.
Conclusions
Recent advances continue to push upstream use of SUS, especially in novel areas like cell therapy. Even as these areas grow, challenges remain. Leachables and extractables remain a concern. Vendors are challenged to ensure proper documentation and product availability while protecting the supply chain and product quality.
Organizations have consistently emphasized the need for SUS devices to be more cost-effective, even as they improve their safety and meet higher expectations of regulators. Both modular and single-use systems present the means to reduce costs, increase productivity, improve quality, reduce risk, and increase flexibility. Using both SUS and modular technology together presents an opportunity for synergy. This may be especially apparent in emerging regions, such as China, where single-use and modular strategies often take a leading role.
Of the nearly 1,600 global bioprocess facilities,2 395, or 25%, are CDMOs. This segment tends to be motivated to get facilities and projects up and running as quickly as possible. They often use disposables to speed up processing and reduce risks of cross-contamination between campaigns. The flexibility and quick turnaround times between process runs and different client projects allowed by single-use equipment can also improve CDMO efficiency, which can reduce their costs.
As the ability to integrate single-use technologies with high-quality modular facilities matures, we expect to see growth across all phases of biomanufacturing.
References:
- 20th Annual Report and Survey of Biopharmaceutical Capacity and Production, BioPlan Associates, Inc. April 2023, Rockville, MD, USA, www.bioplanassociates.com
- Top1000bio Database of Global Biopharmaceutical Facilities, BioPlan Associates, Inc. Accessed September 27, 2023, Rockville, MD, USA, www.Top1000bio.com
About the Author:
 Erica Friedman, a senior research analyst at BioPlan Associates, Inc., has 30 years of experience in research in the pharmaceutical and biotech industries. She has an MLIS from Rutgers University.
Erica Friedman, a senior research analyst at BioPlan Associates, Inc., has 30 years of experience in research in the pharmaceutical and biotech industries. She has an MLIS from Rutgers University.

