Process Development And Scale-Up Of Ceramic Hydroxyapatite
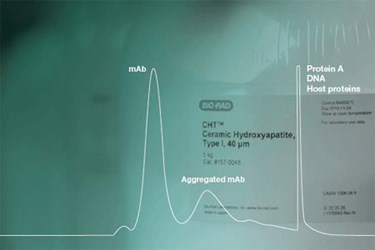
CHT is a leading purification medium of biomolecules in today’s demanding downstream process industry. Its mixed-mode support offers unique selectivities and often separates biomolecules that appear homogeneous with other chromatographic methods. The diverse binding capabilities of CHT for host cell proteins, leached protein A, antibody dimers and aggregates, nucleic acids, and viruses allow its use at any stage from initial capture to final polishing.
Hydroxyapatite, Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, is a form of calcium phosphate used in the chromatographic separation of biomolecules. Sets of five calcium doublets (C-sites) and pairs of –OH containing phosphate triplets (P-sites) are arranged in a repeating geometric pattern. Space-filling models and repeat structure from Raman spectroscopy have also been constructed. Hydroxyapatite has unique separation properties and unparalleled selectivity and resolution. It often separates proteins shown to be homogeneous by electrophoretic and other chromatographic techniques.
Applications of hydroxyapatite chromatography include the purification of:
- Different subclasses of monoclonal and polyclonal
- antibodies
- Antibodies that differ in light chain composition
- Antibody fragments
- Recombinant proteins
- Viral particles
- Vaccines
- Isozymes
- Supercoiled DNA from linear duplexes
- Single-stranded from double-stranded DNA
